Constant charge method or constant potential method: Which is better for molecular modeling of electrical double layers?
Published: JEC
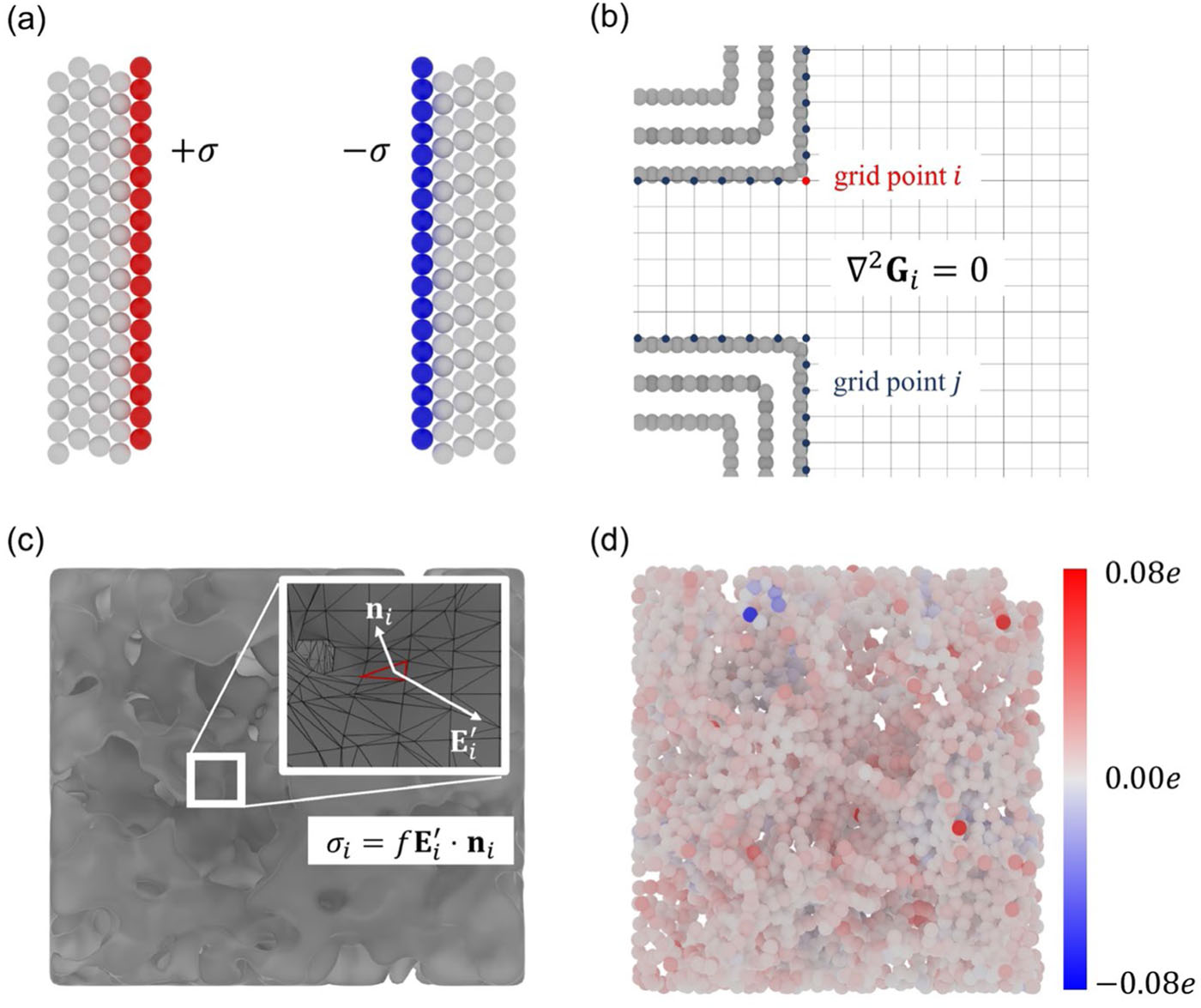
Molecular simulation can accurately depict the atomic-level interface structure of the electric double layer and its dynamic formation process, becoming an essential tool in exploring related fields. In the molecular simulation of the electric double layer, describing electrode polarization is crucial. Constant charge method (CCM) and constant potential method (CPM) are two important approaches. The constant charge method achieves electrode polarization by uniformly distributing charge on the electrode surface, which makes it easier to use and requires fewer computational resources, thus being widely utilized in relevant research. However, the constant charge method does not ensure the physical essence of the electrode being at a constant potential, making it theoretically less accurate. In contrast, the constant potential method maintains the electrode at a constant potential through dynamic changes in electrode atomic charges, aligning more closely with real conditions and yielding more accurate results. However, due to the real-time accurate solution of electrode atomic charges, the constant potential method requires nearly an order of magnitude more computational resources.

Citation: Liang Zeng, Xi Tan, Xiangyu Ji, Shiqi Li, Jinkai Zhang, Jiaxing Peng, Sheng Bi, Guang Feng*. Constant charge method or constant potential method: Which is better for molecular modeling of electrical double layers? Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 94, 54.
Paper Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095495624001694